Wire, as commercially produced, is not straight. The desired curvature should always be considered, and in some instances actually specified.
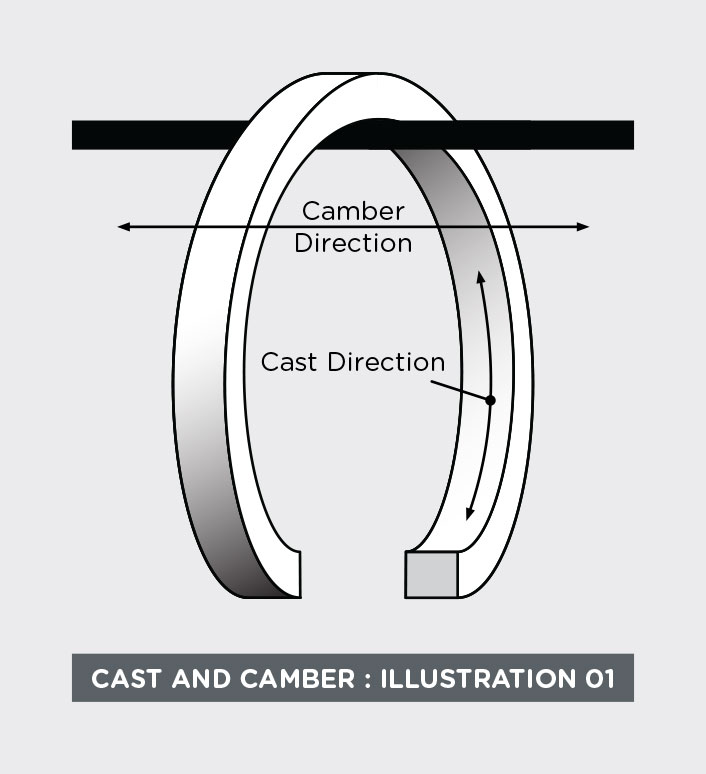
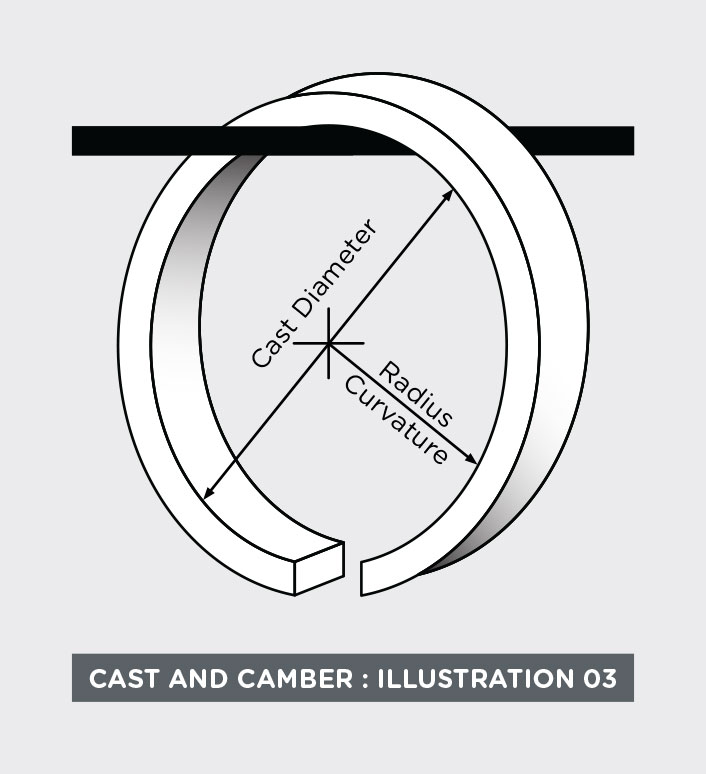
The curvature of the wire has two components: Radial and Axial. The Radial, or circular, curvature is called “cast.” Cast is measured as the diameter of a free turn of wire or as a radius of curvature.
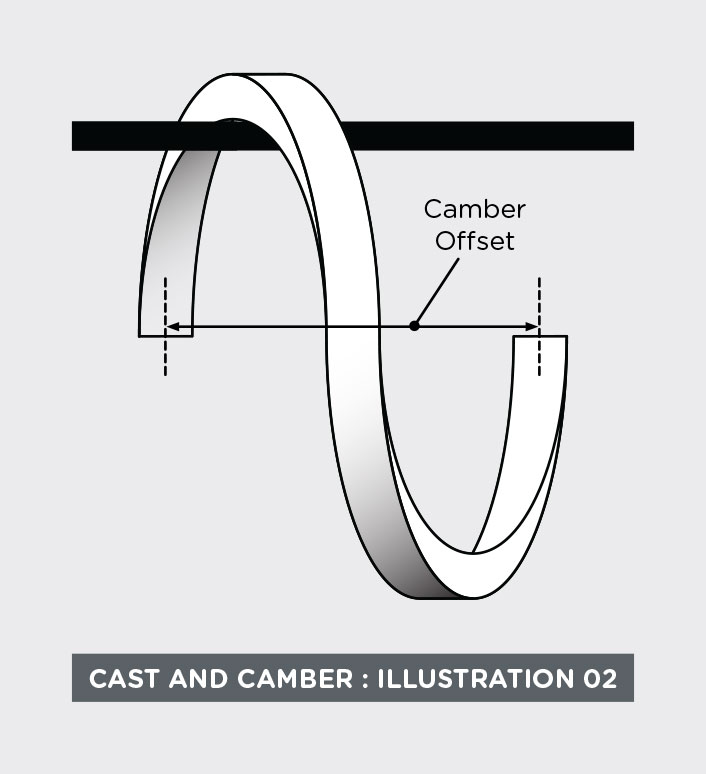
The axial component is called “camber.” Camber may be measured as the offset in the ends of one turn of freely hanging wire.
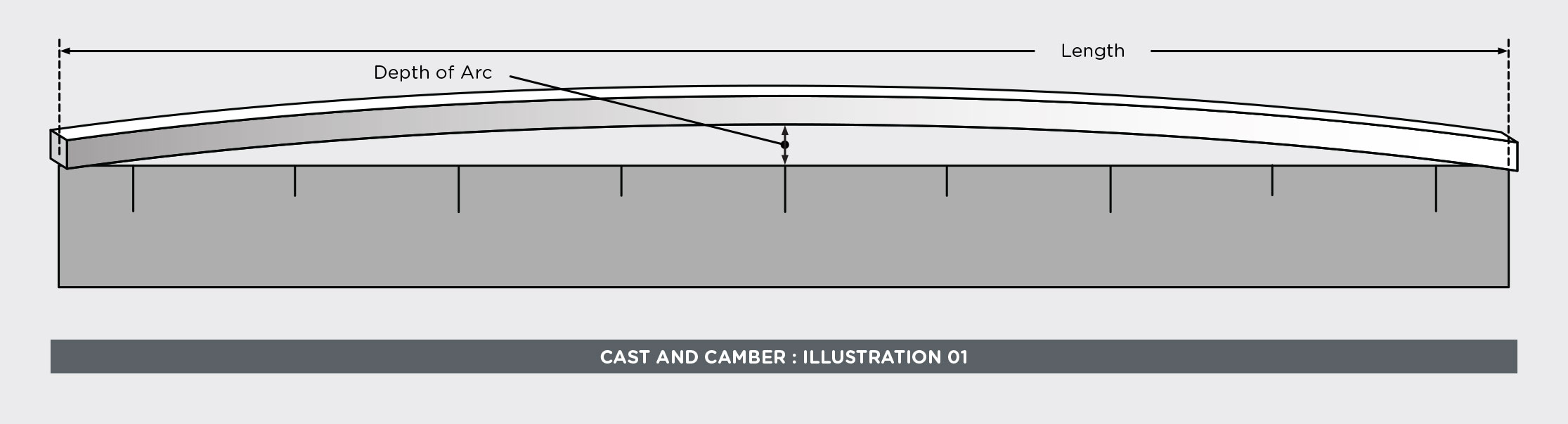
If the cast specified is extremely straight, the camber may be measured by placing a reference length of wire on a flat surface and against a straight edge. The greatest measurement between the straight edge and the wire is the “depth of arc,” which is a measurement of camber.
Regardless of cast and camber required, they must always be uniform throughout the length of wire.
